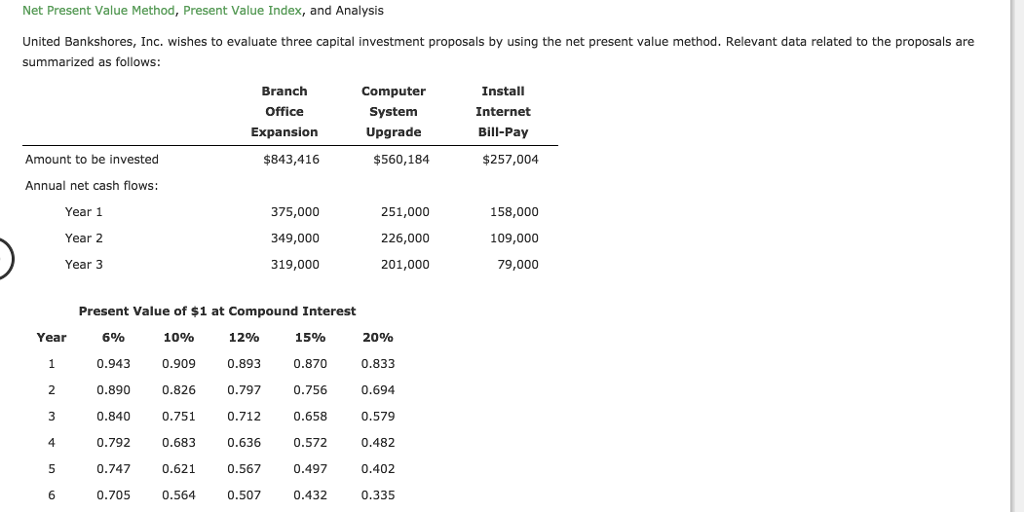
Inaccurate projections can lead to misleading NPV results and suboptimal decision-making. Finally, subtract the initial investment from the sum of the present values of all cash flows to determine the NPV of the investment or project. Using the discount rate, calculate the present value of each cash flow by dividing the cash flow by (1 + discount rate) raised to the power of the period in which the cash flow occurs. This calculation will provide the present value of each cash flow, adjusted for the time value of money.
Interest Rates
It also assumes that cash flows will be received at regular intervals, which may not always be the case. Additionally, NPV does not take into account non-financial factors such as risk, which can also impact investment decisions. Present value is important in order to price assets or investments today that will be sold in the future, or which have returns or cash flows that will be paid in the future. Because transactions take place in the present, those future cash flows or returns must be considered by using the value of today’s money. Present Value is a fundamental concept in finance that enables investors and financial managers to assess and compare different investments, projects, and cash flows based on their current worth.
Determine the Discount Rate
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional. This present value calculator can be used to calculate the present value of a certain amount of money in the future or periodical annuity payments.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
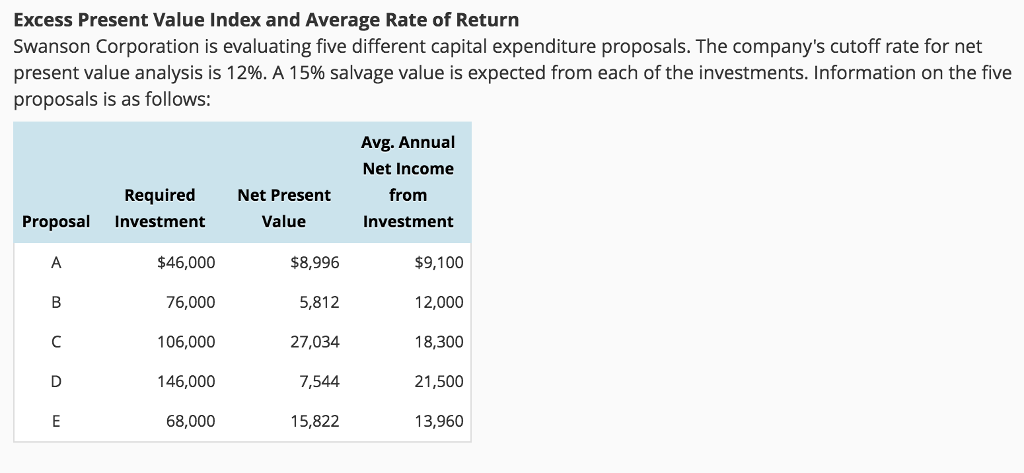
The PVI helps companies evaluate whether an investment is worth it financially, and if it will generate a positive return. It involves assessing the potential projects at hand and budgeting their projected cash flows. Once in place, the present value of these cash flows is ascertained and compared between each project. Typically, the project that offers the highest total net present value is selected, or prioritized, for investment. The EPV can be used to make more accurate decisions when assessing investments and financial decisions, allowing for more informed decision-making.
Incorporates Time Value of Money
A mentioned, the discount rate is the rate of return you use in the present value calculation. It represents your forgone rate of return if you chose to accept an amount in the future vs. the same amount today. The discount rate is highly subjective because it’s simply the rate of return you might expect to receive if you invested today’s dollars for a period of time, which can only be estimated.
Understanding PV is essential for making informed decisions about the allocation of resources and the evaluation of investment opportunities. This is because of the potential earnings that could be generated if the money were invested or saved. We’ll assume a discount rate of 12.0%, a time frame of 2 years, and a compounding frequency of one.
- The present value (PV) formula discounts the future value (FV) of a cash flow received in the future to the estimated amount it would be worth today given its specific risk profile.
- Therefore, to have an accurate assessment of how much the future cash flow is worth today, you must incorporate the rate of inflation into your discount rate.
- The discount rate is highly subjective because it’s simply the rate of return you might expect to receive if you invested today’s dollars for a period of time, which can only be estimated.
- Projects that require large investments typically have tighter profit margins, which may result in lower PVI results.
- NPV takes into account both the magnitude and timing of cash flows, providing a more accurate representation of an investment or project’s profitability compared to other methods that may not consider these factors.
Given a higher discount rate, the implied present value will be lower (and vice versa). The present value (PV) concept is fundamental to corporate finance and valuation. For example, $1,000 today should be worth more than $1,000 five years from now because today’s $1,000 can be invested for those five years and earn a return.
Yes, the equipment should be purchased because the net present value is positive ($1,317). Having a positive net present value means the project promises a rate of return that is higher than the minimum rate of return required by management (20% in the above example). The management of Fine Electronics Company is considering to purchase an equipment to be attached with the main manufacturing machine. On this page, first we would net fixed assets formula explain what is net present value and then look into how it is used to analyze investment projects in capital budgeting decisions. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
By comparing NPVs, decision-makers can identify the most attractive investment opportunities and allocate resources accordingly. For example, if your payment for the PV formula is made monthly, then you’ll need to convert your annual interest rate to monthly by dividing by 12. Also, for NPER, which is the number of periods, if you’re collecting an annuity payment monthly for four years, the NPER is 12 times 4, or 48.
Therefore, the real return on real estate investment might be higher than that of the bond. It is essentially the interest rate used to depreciate future income, and its accurate estimation is paramount. However, determining an appropriate discount rate is challenging due to the numerous factors involved – risk-free rate, inflation expectations, risk premium, and more. Present value calculations in CSR initiatives also extend to considering future stakeholder value.
